Difference between revisions of "Category:Function-Modul"
m (→Mobile transmitter mode) |
m (Redirected page to Category:Function moduls, Function decoders) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | #REDIRECT [[Category: Function moduls, Function decoders]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:dc-car5.jpg|420px|thumb|right|Function modul]] | ||
| + | [[File:lichtanaus.png|430px|thumb|right|Light on / off]] | ||
==Function Modules== | ==Function Modules== | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
| Line 4: | Line 8: | ||
There are always 8 outputs available.<br> | There are always 8 outputs available.<br> | ||
By using a dipswitch 10 different module types are available<br> | By using a dipswitch 10 different module types are available<br> | ||
| − | Supply voltage can be | + | Supply voltage can be 12V - 16V AC or 12 - 16V DC<br> |
The outputs offer a current of 1A<br> | The outputs offer a current of 1A<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
By using a diode-circuit with 1N400x diodes it is possible to transmit multiple commands on one IR LED.<br> | By using a diode-circuit with 1N400x diodes it is possible to transmit multiple commands on one IR LED.<br> | ||
| − | ===Stop module=== | + | ===Stop module (All switches ON)=== |
| − | All switches | + | All switches ON |
Stop module means all 8 outputs sending a stop signal | Stop module means all 8 outputs sending a stop signal | ||
| Line 74: | Line 78: | ||
| − | + | ===Remote control mode I (all off)=== | |
| − | ===Remote control mode=== | + | All links (jumpers) or switches OFF |
| − | All links (jumpers) or switches | + | |
Now at the outputs the commands of a mobile transmitter are available<br> | Now at the outputs the commands of a mobile transmitter are available<br> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 92: | ||
A2 running light 1 (with CV60 light 1, 2, 3 and 4 at the same time possible)<br> | A2 running light 1 (with CV60 light 1, 2, 3 and 4 at the same time possible)<br> | ||
H6 flashing blue-lights and front-flashers with siren (alternative: switch to continuous light for another two lights)<br> | H6 flashing blue-lights and front-flashers with siren (alternative: switch to continuous light for another two lights)<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Function Module J (Dipswitch 1+2)=== | ||
| + | up 1.Sep.2016 | ||
| + | '''Additional lights'''<br> | ||
| + | Dipswitch 1+2 must be set ON<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1 = (MF3) ON<br> | ||
| + | 2 = (MF3) OFF<br> | ||
| + | 3 = (MF4) ON<br> | ||
| + | 4 = (MF4) OFF<br> | ||
| + | 5 = (MF5) ON<br> | ||
| + | 6 = (MF5) OFF<br> | ||
| + | 7 = Speed at speed step 0<br> | ||
| + | 8 = Speed at speed step 0<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Function Module SW== | ==Function Module SW== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 128: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==IR-LED on/in the street == | ==IR-LED on/in the street == | ||
Mounting of the IR-LED on the site: | Mounting of the IR-LED on the site: | ||
| − | The IR-LED is placed in or nearby the street in such a way that the cars can "see" the IR- | + | The IR-LED is placed in or nearby the street in such a way that the cars can "see" the IR-light, emitted by the LED and execute the transmitted function at the intended place.<br> |
| − | The IR-LED must be adjusted in a way, that the approaching vehicles | + | The IR-LED must be adjusted in a way, that the approaching vehicles can "see" it. On a straight line the vehicles detect the desired function in a distance of approx. 5 - 15cm from the LED<br> |
Sometimes a IR-LED influences the traffic on a parallel line too. In this case you can either increase the series resistor to decrease the range of the IR-signal or mount the LED into the street in a way that its IR beam lights vertical only. | Sometimes a IR-LED influences the traffic on a parallel line too. In this case you can either increase the series resistor to decrease the range of the IR-signal or mount the LED into the street in a way that its IR beam lights vertical only. | ||
| − | If | + | If you do the second, please use LED with a wider angle of reflection. |
Distance of the LEDs shoul be 5 - 10cm, but it is highly recommended to test it in every single case! | Distance of the LEDs shoul be 5 - 10cm, but it is highly recommended to test it in every single case! | ||
| Line 169: | Line 142: | ||
Using cars with a significiant lag it can be neccessary to use more LEDs | Using cars with a significiant lag it can be neccessary to use more LEDs | ||
| − | The LEDs are | + | The LEDs are connected to the same connector, each ussing its own series resistor. |
==Mobile Transmitter SW== | ==Mobile Transmitter SW== | ||
| Line 215: | Line 188: | ||
other functions still can be controlled by switches<br> | other functions still can be controlled by switches<br> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Function moduls, Function decoders]] |
| − | + | ||
[[Category:Software]] | [[Category:Software]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Instructions]] | [[Category:Instructions]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Source_of_supply_UK]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Source_of_supply_US]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Index_UK]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Index_US]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:10, 6 August 2017
Redirect to:
Contents
Function Modules
General
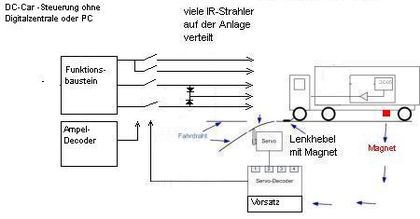
A function module transmits commands to a DC-Car Decoder by means of a short ranche IR communication (10-20cm).
There are always 8 outputs available.
By using a dipswitch 10 different module types are available
Supply voltage can be 12V - 16V AC or 12 - 16V DC
The outputs offer a current of 1A
By using a diode-circuit with 1N400x diodes it is possible to transmit multiple commands on one IR LED.
Stop module (All switches ON)
All switches ON Stop module means all 8 outputs sending a stop signal
Function Module A
Basic Commands
Dipswitch 1 must be set ON
1 = Speed at speed step 0 (stop)
2 = headlights 1 ON
3 = headlights 1 OFF
4 = Left indicator ON
5 = Right indicator ON
6 = Indicators OFF
7 = Speed at speed step 14
8 = Speed at speed step 28
Function Module B
Flashing Blue light vehicles
Dipswitch 2 must be set ON
1 = Speed at speed step 0 (stop)
2 = Hazard lights on
3 = Hazard kights OFF
4 = Flashing blue-light ON
5 = Flashing blue-light OFF
6 = Front-flasher ON
7 = Front-flasher OFF
8 = Speed at speed step 28
Function Module C
Additional lights and speed
Dipswitch 3 must be set ON
1 = Light 2 ON
2 = Light 2 OFF
3 = Light 3 ON
4 = Light 3 OFF
5 = Speed + 2 steps (accelerate)
6 = Speed - 2 steps (slowdown)
7 = Speed at speed step 10
8 = Speed at speed step 21
Function Module D
special functions
Function Module E
automatic module
Function Module F
special functions
Function Module G
Flashing blue-light vehicles
Function Module H
standard collection
Remote control mode I (all off)
All links (jumpers) or switches OFF
Now at the outputs the commands of a mobile transmitter are available
Collection as mobile transmitter:
the chip has been collected with the functions of the different modules. The letter marks the module, the number its output connector.
D1 time-controlled stop (programmed via CV108) blinker OFF
D5 run-up after stop (time is out) with drive position from CV110 (z.B. 1) blinker OFF
C5 speed +2 (accelerate CV 98)
H2 all lights OFF
A4 blinker left (with CV27=64 blinker right + left (same time) = anti-collision-lights possible)
A5 blinker right (with CV27=64 blinker right + left (same time) = anti-collision-lights possible)
A2 running light 1 (with CV60 light 1, 2, 3 and 4 at the same time possible)
H6 flashing blue-lights and front-flashers with siren (alternative: switch to continuous light for another two lights)
Function Module J (Dipswitch 1+2)
up 1.Sep.2016
Additional lights
Dipswitch 1+2 must be set ON
1 = (MF3) ON
2 = (MF3) OFF
3 = (MF4) ON
4 = (MF4) OFF
5 = (MF5) ON
6 = (MF5) OFF
7 = Speed at speed step 0
8 = Speed at speed step 0
Function Module SW
This module combines the functions of all modules in one.
All links (jumpers) or switches 1 - 8 OFF: all outputs transmit drive position 0 (8 times stop module)
All links (jumpers) or switches 1 - 8 ON: 8 mobile transmitter commands
Link(jumper) or switch "ON":
0 = stop no link
1 = FB-A link 19-9
2 = FB-B link 19-8
3 = FB-C link 19-7
4 = FB-D link 19-6
5 = FB-E link 19-5
6 = FB-F link 19-4
7 = FB-G link 19-3
8 = FB-H link 19-2
all = mobile transmitter mode
IR-LED on/in the street
Mounting of the IR-LED on the site:
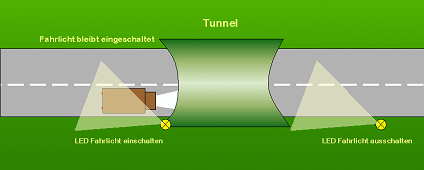
The IR-LED is placed in or nearby the street in such a way that the cars can "see" the IR-light, emitted by the LED and execute the transmitted function at the intended place.
The IR-LED must be adjusted in a way, that the approaching vehicles can "see" it. On a straight line the vehicles detect the desired function in a distance of approx. 5 - 15cm from the LED
Sometimes a IR-LED influences the traffic on a parallel line too. In this case you can either increase the series resistor to decrease the range of the IR-signal or mount the LED into the street in a way that its IR beam lights vertical only.
If you do the second, please use LED with a wider angle of reflection.
Distance of the LEDs shoul be 5 - 10cm, but it is highly recommended to test it in every single case!
When the car passes the first LED it will start slowing down - an when it reaches the second LED in most cases it is that slow,
that it can come to a stop right there.
Using cars with a significiant lag it can be neccessary to use more LEDs
The LEDs are connected to the same connector, each ussing its own series resistor.
Mobile Transmitter SW
Using a more complex circuit, more commands of the SW function module are usable.
For complexity and error rate are to high for self-construction, our mobile transmitters are produced in series
Actually tthe first upgrades are available:
- charge connector is designed for 11 - 13V
on the other hand the charge connector delivers low voltage/current so it can be used for testing LED
- this connector can be extended for use as a continuity tester
LED test function is still available using this feature but another LED shows continuity
- solder a phototransistor to a plug and plug this into the jack
when the phototransistor is lighted, the LED of the continuity tester will glow
So you can check the IR-signals of the DC-Car System anytime
- possible extensions
with a built-in DC06 decoder, all signals could be shown by indicator lamps/LED
this wouuld enable you to check if in fact, a mixed signal is transmitted or a single signal only
this would make the mobile transmitter to a unversal tool for the DC-Car System
Function Decoder
Using the function module in DCC mode with a digital central
A function module can be extended with a digital input
After extension with a digital input the finction module becomes a function decoder
This enables switching the 8 outputs from a digital central using the addresses 1-8 (9-15)
Gerade in der Kombination mit anderen Funktionen macht das Schalten des Lichtausgang Sinn.
The decoder can be usd the same way as the module but offers switching by using 8 sequenced adresses
- central switching of "stop" for emergency OFF
- central switching of light for day-/night mode
Blinkers are controlled by feedback sensors of junctions, lights are controlled by a digrital address
day/night control with a function decoder
Tag / Nachtsteuerung mit einem Funktionsdecoder.
other functions still can be controlled by switches
Pages in category "Function-Modul"
The following 17 pages are in this category, out of 17 total.
ACI |
I cont.S |
S cont.TW |